Introduction
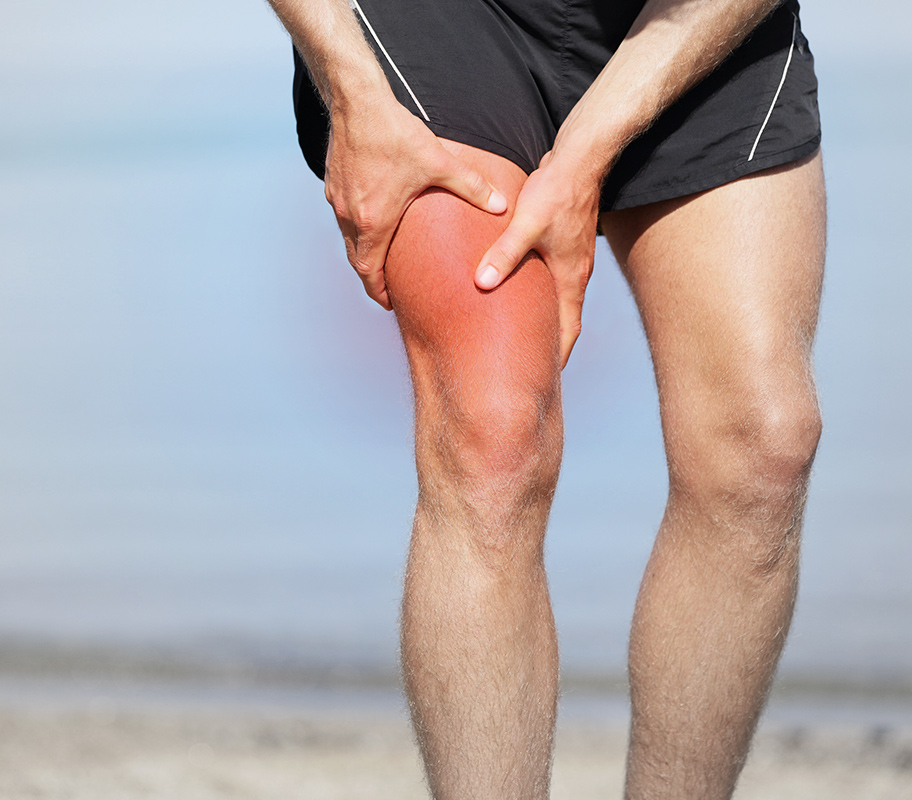
Upper thigh pain may be severe, interfering with everyday tasks and lowering quality of life. In this detailed guide, we will look at the numerous causes, symptoms, and treatment options for upper thigh discomfort to give you useful information and help.
Tapentadol 200mg is a larger dose of the medicine used to treat moderate to severe pain. Tapentadol 200mg, like the 100mg dosage, is an opioid analgesic. Its mode of action includes binding to the mu-opioid receptor and blocking norepinephrine reuptake, resulting in dual pain relief benefits.

Causes of Upper Thigh Pain:
1. Muscle strain.
Muscle strain, which is often caused by overuse or rapid movements, may cause discomfort in the upper thigh. Running, leaping, and carrying large things may all put a strain on these muscles.
2. Overuse Injuries.
Repetitive motions or misuse of the thigh muscles without enough recovery may lead to overuse injuries, which cause pain and discomfort. Athletes and those working in physically demanding jobs are more vulnerable to such accidents.
3. Nerve compression.
Nerve compression in the thigh area, such as the sciatic or femoral nerve, may result in radiating pain in the upper thigh. Conditions such as herniated discs or sciatica may cause nerve compression and associated pain.
4) Tendonitis
Tendonitis, an inflammation of the tendons that link muscles to bones, may develop in the thigh as a result of repeated stress or injury. This disease often causes discomfort, soreness, and swelling in the afflicted region.
5) Bursitis
Bursitis, or inflammation of the bursae (fluid-filled sacs that cushion the joints), may occur in the hip or thigh area. Overuse, trauma, or underlying medical issues may cause bursitis, resulting in discomfort and reduced movement.
6. Fractures.
Fractures or fractures in the thigh bones, such as the femur, may result in significant discomfort and limited movement. Traumatic injuries, falls, or accidents are typical causes of thigh bone fractures, which need immediate medical treatment.
7. Arthritis
Arthritis, which includes osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, may cause persistent pain, stiffness, and swelling in the hips and thighs. Degenerative alterations in joint tissues lead to the worsening of arthritis symptoms.
8. Vascular Conditions.
Vascular diseases including deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or peripheral artery disease (PAD) may cause pain and discomfort in the upper thigh. Vascular-related thigh discomfort might be caused by reduced blood flow or the development of a blood clot.
9. Infections
Infections of the thigh muscles, joints, or bones may result in localised discomfort, edoema, and redness. Bacterial, viral, or fungal infections may need medical intervention, such as antibiotics or antifungal drugs.
Tapentadol 100mg is a medicine used to relieve moderate to severe pain. It is an opioid analgesic. The major method of action is to bind to the mu-opioid receptor and impede norepinephrine reuptake. This multimodal mechanism helps manage pain by influencing both the opioid and noradrenergic pathways.

Symptoms Of Upper Thigh Pain
Buy tapentadol online is a centrally acting analgesic (pain reliever) that treats moderate to severe pain. It is classed as an opioid analgesic and comes in both immediate and extended-release forms. Tapentadol binds to mu-opioid receptors in the central nervous system and inhibits norepinephrine reuptake.
Treatment Options for Upper Thigh Pain.
1. Rest and Ice.
Resting the afflicted leg and using ice packs may help relieve the discomfort and inflammation caused by muscular strains, overuse injuries, or acute trauma.
2. Pain medications
Over-the-counter pain medications, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, may help with mild to severe thigh discomfort. Prescription drugs may be required for severe or ongoing pain.
3. Physical Therapy.
Physical therapy procedures such as stretching, strengthening, and manual treatment may assist improve thigh muscle flexibility, strength, and range of motion.
4. Injections.
Steroid or corticosteroid injections may be used to relieve inflammation and discomfort in the thigh, notably for tendonitis or bursitis.
5. Bracing or Support.
Wearing a brace or supporting device may help to stabilise and reduce strain on the thigh muscles and joints, aiding healing and avoiding future damage.
6. Surgical intervention
In the event of severe injuries, fractures, or underlying structural problems, surgical intervention may be required to heal damaged tissues, realign bones, or treat other contributing causes.
7. Lifestyle Modifications
Making lifestyle modifications, such as keeping a healthy weight, using good body mechanics, and avoiding activities that aggravate thigh discomfort, may help prevent recurring problems and boost overall musculoskeletal health.
8. Alternative therapies.
Acupuncture, massage therapy, and chiropractic treatment may provide further comfort for those who have chronic or recurrent thigh pain.
9. Medical Management.
Seeking immediate medical examination and management is critical for precisely identifying the underlying cause of thigh pain and executing suitable treatment techniques based on individual requirements.
Conclusion
Upper thigh discomfort may have a substantial influence on a person’s movement, comfort, and general health. Understanding the numerous causes, symptoms, and treatment choices discussed in this article allows people to take proactive efforts to successfully manage thigh pain and recover control of their health and mobility.