Seeing Spots? The Solution to Irregularly Shaped Patches with Gingival Depigmentation
Intro
Are you noticing irregularly shaped patches of discoloration on your gums? If so, you may be experiencing gingival depigmentation. This condition is caused by an overproduction of melanin in the body and can lead to broad, deep purplish discoloration or brown, light brown, or black patches. Thankfully, there are solutions to treating this condition. In this blog post, we’ll explore the process of gingival depigmentation, its symptoms, and how you can treat it.
Understanding Gingival Depigmentation
Gingival depigmentation is a condition that affects the gums, causing irregularly shaped patches of discoloration. Understanding this condition is essential to finding effective solutions and treatments. When the body produces an excessive amount of melanin, the pigment responsible for the color of our skin and gums, it can lead to gingival depigmentation. This overproduction can result in deep purplish discoloration or patches that range in color from brown to light brown or black.
Gingival depigmentation can be an aesthetic concern for many individuals, causing self-consciousness and a desire for treatment. Thankfully, there are several options available to address this condition, including laser treatment, surgical removal, or the use of chemical agents to lighten the affected areas.
By understanding the causes and symptoms of gingival depigmentation, individuals can seek appropriate treatment and make informed decisions about their oral health. With the right knowledge, prevention, and maintenance strategies, it is possible to minimize the appearance of discoloration and maintain healthy gums. Stay tuned to explore the various causes, symptoms, and treatment options for gingival depigmentation in the upcoming sections.

Causes of Gingival Discoloration
Gingival discoloration can be caused by various factors, including genetics, certain medications, and lifestyle habits. Genetics play a significant role in determining the color of our gums, so individuals with a family history of gingival discoloration are more likely to experience it themselves. Additionally, certain medications, such as antimalarials and certain antibiotics, can cause gum discoloration as a side effect. Lifestyle habits, such as smoking or tobacco use, can also contribute to gingival discoloration.
Another potential cause of gingival discoloration is oral health conditions. For example, individuals with gum disease or poor oral hygiene may develop dark patches or discoloration on their gums. Certain systemic diseases, like Addison’s disease or Peutz-Jeghers syndrome, can also lead to gingival discoloration.
Lastly, hormonal changes, such as those that occur during pregnancy or puberty, can affect melanin production and lead to gum discoloration.
It’s important to consult with a dental professional to determine the underlying cause of gingival discoloration and develop an appropriate treatment plan. They can assess your medical history, perform a thorough examination, and provide personalized recommendations to address the discoloration effectively.
Common Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the symptoms of gingival depigmentation is crucial in order to seek appropriate treatment. While the most obvious symptom is the irregularly shaped patches of discoloration on the gums, there are other signs to look out for as well.
Some individuals may experience gum sensitivity or discomfort in the areas where the discoloration is present. Others may notice a change in the texture of the affected gums, such as a rough or bumpy surface. In more severe cases, there may be bleeding or inflammation around the discolored patches.
Diagnosing gingival depigmentation typically involves a visual examination by a dental professional. They will closely inspect the gums and ask about any symptoms or concerns. In some cases, a biopsy may be necessary to rule out other underlying conditions.
If you suspect that you have gingival depigmentation, it is important to schedule an appointment with a dentist or periodontist. They can provide an accurate diagnosis and recommend the most appropriate treatment plan based on your specific case. Early detection and treatment can help restore the natural color of your gums and improve your overall oral health.
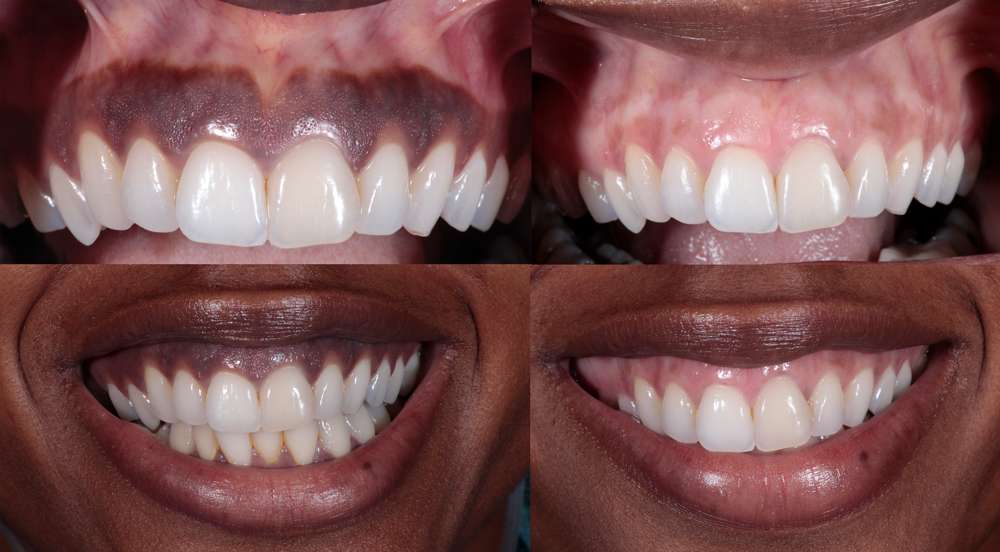
Treatment Options for Gingival Depigmentation
Treating gingival depigmentation involves various options depending on the severity and individual preferences. One common treatment option is laser treatment, which uses laser energy to remove the pigmented cells and stimulate the regeneration of healthy tissues. This non-invasive procedure is precise, effective, and minimizes discomfort during and after treatment.
Surgical removal is another option, particularly for more extensive cases. This involves physically removing the pigmented tissue using scalpels or electrosurgery, and then allowing the gums to heal naturally. While this procedure may require more downtime and can cause temporary discomfort, it can effectively remove deep and stubborn pigmentation.
Chemical agents can also be used to lighten the affected areas. These agents are applied topically and work by breaking down the excess melanin and gradually lightening the discoloration. This option is less invasive than surgery but may require multiple treatments to achieve desired results.
It is important to consult with a dental professional to determine the most suitable treatment option for your specific case. They can assess the severity of your depigmentation and discuss the pros and cons of each treatment option. With proper treatment, you can achieve a more uniform and aesthetically pleasing gum appearance.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Changes
While professional treatments offer effective solutions for gingival depigmentation, there are also home remedies and lifestyle changes you can incorporate into your daily routine to help improve the appearance of your gums.
1. Proper oral hygiene: Maintaining good oral hygiene is crucial in preventing and managing gingival discoloration. Brush your teeth at least twice a day and floss daily to remove plaque and bacteria that can contribute to gum problems. Consider using a soft-bristled toothbrush and a gentle toothpaste to avoid irritating the gums.
2. Quit smoking: If you’re a smoker, quitting smoking is not only beneficial for your overall health, but it can also help improve the appearance of your gums. Smoking not only contributes to gingival discoloration but also increases the risk of gum disease, which can worsen the condition.
3. A healthy diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables can promote healthy gums. Foods high in vitamin C, such as citrus fruits and leafy greens, can help strengthen gum tissues and reduce discoloration. Avoiding sugary snacks and drinks can also prevent plaque buildup and maintain gum health.
4. Avoid excessive caffeine and dark beverages: Beverages like coffee, tea, and red wine can stain the teeth and potentially contribute to gingival discoloration. Limit your consumption of these beverages or use a straw to minimize contact with the gums.
5. Stress management: Chronic stress can negatively affect oral health, including the appearance of your gums. Finding healthy ways to manage stress, such as practicing yoga, meditation, or engaging in hobbies, can contribute to overall gum health.
While these home remedies and lifestyle changes can help improve the appearance of your gums, it’s important to remember that professional treatments may still be necessary for severe cases of gingival depigmentation. Consult with your dental professional to determine the best approach for your individual needs.
Tips for Prevention and Maintenance
Taking steps to prevent and maintain the appearance of your gums can go a long way in minimizing the risk of gingival depigmentation. Here are some helpful tips to incorporate into your daily routine:
1. Practice good oral hygiene: Brush your teeth at least twice a day and floss daily to remove plaque and bacteria that can contribute to gum problems. Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and a gentle toothpaste to avoid irritating the gums.
2. Quit smoking: Besides its detrimental effects on overall health, smoking can contribute to gingival discoloration and increase the risk of gum disease. Quitting smoking can improve the appearance of your gums and overall oral health.
3. Eat a healthy diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables can promote healthy gums. Vitamin C-rich foods, like citrus fruits and leafy greens, can strengthen gum tissues and reduce discoloration. Avoid sugary snacks and drinks to prevent plaque buildup and maintain gum health.
4. Limit dark beverages: Beverages like coffee, tea, and red wine can stain the teeth and potentially contribute to gingival discoloration. Limit your consumption or use a straw to minimize contact with the gums.
5. Manage stress: Chronic stress can negatively affect oral health, including the appearance of your gums. Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as practicing yoga, meditation, or engaging in hobbies that help you relax.
By following these tips, you can significantly reduce the risk of gingival depigmentation and maintain healthy and aesthetically pleasing gums. However, it’s important to remember that professional treatments may still be necessary for severe cases. Consult with your dental professional to determine the best approach for your individual needs.


